Saturday, July 10, 2010
Hydrogen Bomb! - KABOOOM!!


-Also known as thermonuclear bomb
-Hydrogen bomb or H-bomb is a weapon deriving a large portion of its energy from the nuclear fusion of hydrogen isotopes. In an atomic bomb, uranium or plutonium is split into lighter elements that together weigh less than the original atoms , the remainder of the mass appearing as energy. Unlike this fission bomb, the hydrogen bomb functions by the fusion, or joining together, of lighter elements into heavier elements. The end product again weighs less than its components, the difference once more appearing as energy. Because extremely high temperatures are required in order to initiate fusion reactions.


10:23 PM
Orbital Theories
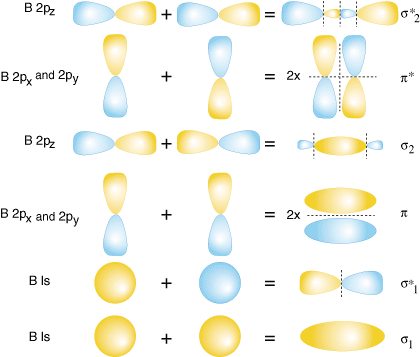
-Molecular orbital theory is a method for determining molecular structure in which electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms, but treated as moving under the influence of the nuclei in the whole molecule.
-In this theory, each molecule has a set of molecular orbitals, in which it is assumed that the molecular orbital wave function ψf may be written as a simple weighted sum of the n constituent atomic orbitals χi , according to the following equation: 

-The cij coefficients may be determined numerically by substitution of this equation into the Schrödinger equation and application of the variational principle. This method is called the linear combination of atomic orbitals approximation and is used in computational chemistry. An additional unitary transformation can be applied on the system to accelerate the convergence in some computational schemes.

9:23 PM
Friday, July 9, 2010
ISOTOPES
What are isotopes?



What are isotopes?
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different number of neutrons.
Examples of Isotopes:
Hydrogen.
Hydrogen has no neutrons at all but there is also a hydrogen isotope called deuterium with one neutron and tritium with two neutrons.

Radioactive Isotopes
-Also known as radioisotopes
-Are atoms with a different number of neutrons than a usual atom with an unstable nucleus that decays, emitting alpha, beta and gamma rays until the isotope reaches stability. Once it is stable, the isotope becomes another element entirely. Radioactive decay is spontaneous so it is often hard to know when it will take place or what sort of rays it will emit during decay.
-There are around 3800 radioactive isotopes. 200 radioactive isotopes used on a regular basis. While some are found in nature, most others have to be manufactured to suit specific needs, such as for hospitals , research labs and manufacturers.
-Radioactive isotopes can be manufactured in several ways, the most common by neutron activation in a nuclear reactor which involves capturing a neutron by the nucleus of an atom which results in an excess of neutrons. Some radioactive isotopes are produced in a cyclotron in which protons are introduced to a nucleus resulting in a deficiency of neutrons.
-Radioactive isotopes have very useful properties. Alpha, beta and gamma radiation can permeate solid objects like an x-ray, but are progressively absorbed by them. The amount of penetration depends on a several factors including the energy of the radiation, mass of particle, and density of the solid. These properties can lead to many uses for radioisotopes in the scientific, medical, archaeological and industrial fields. The uses of radioactive isotopes in these fields depend on what element they become after they reach stability.



11:00 PM
Tuesday, July 6, 2010
ATOMS
-Are made up of neutrons, protons and electrons.
-The central nucleus is surrounded by negatively charged electrons.
-The atomic nucleus contains positively charged protons and neutral neutrons.

3:18 PM
